As global healthcare shifts toward personalized, preventive, and patient-centric models, the demand for fast, accurate, and accessible diagnostic solutions is increasing. Chronic non-communicable diseases — including cardiovascular disease, diabetes mellitus, anemia, and gout — are now leading contributors to global morbidity and mortality. These conditions often develop silently and are diagnosed late, leading to preventable complications.
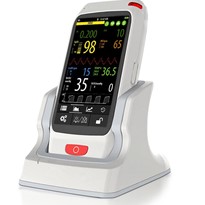
Early detection and continuous monitoring of key blood biomarkers is a proven strategy to reduce disease burden and improve outcomes. In response to this need, we introduce a multi-parameter, point-of-care blood testing system that combines cutting-edge biosensor technology, microfluidics, and intelligent data processing to rapidly measure Total Cholesterol, Blood Glucose, Hemoglobin, and Uric Acid from a small capillary blood sample — right at the point of care or home.
1. Clinical Relevance of Measured Parameters
Each biomarker included in this system provides clinically actionable insights and supports early intervention:
- Total Cholesterol: A major predictor of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD), elevated cholesterol contributes to plaque buildup and arterial narrowing. Routine lipid monitoring enables clinicians to stratify cardiovascular risk and adjust statins or lifestyle interventions.
- Blood Glucose: A cornerstone of diabetes diagnosis and management, glucose levels require close monitoring to prevent hypo- or hyperglycemia. Real-time glucose readings support decisions on insulin dosing, diet, and physical activity.
- Hemoglobin (Hb): A direct marker of anemia, hemoglobin levels help diagnose nutritional deficiencies, chronic diseases, and bleeding disorders. Monitoring is essential in pregnancy, chronic kidney disease, and cancer-related therapies.
- Uric Acid: Elevated serum uric acid is associated with gout, nephrolithiasis, and metabolic syndrome. Timely testing supports pharmacological titration and lifestyle management to prevent crystal deposition and renal injury.
2. System Architecture and Technology
The system integrates biosensing chemistry with smart electronics in a compact, user-friendly format:
- Sample Collection: Capillary blood via fingertip prick; Volume: ~10–20 µL
- Measurement Mechanisms:
• Electrochemical biosensors (Glucose, Uric Acid): Enzyme-based redox reaction measured via amperometry
• Photometric analysis (Hemoglobin, Cholesterol): Light absorption at specific wavelengths for colorimetric quantification
- Device Core & Processing: Embedded microcontroller with signal conditioning; proprietary calibration algorithms per test strip lot
- User Interface: Integrated LCD or touchscreen display; optional smartphone app
- Connectivity & Integration: Bluetooth/Wi-Fi module for EMR and telemonitoring
- Power Source: Rechargeable Li-ion battery or replaceable batteries;
3. Applications and Use Cases
This versatile platform is engineered for diverse clinical and field environments:
- Home Monitoring
- Primary Care Clinics
- Rural and Low-Infrastructure Settings
- Workplace & Occupational Health
- Pharmacies and Diagnostic Kiosks
4. Advantages Over Traditional Lab Testing
|
Feature |
Conventional Lab Testing |
Smart Multi-Parameter System |
|
Turnaround Time |
24–72 hours |
2 minutes or less |
|
Sample Type |
Venous blood |
Capillary (fingerstick) |
|
Location |
Centralized lab |
Home or point-of-care |
|
Result Access |
Paper/email reports |
Digital, real-time |
|
Cost Efficiency |
High per test |
Economical in bulk |
|
Follow-up Speed |
Delayed |
Immediate intervention possible |
|
Data Integration |
Manual |
EMR-compatible, app-based |
Conclusion
This next-generation Blood Parameter Monitoring System is a transformative leap in preventive diagnostics. By unifying four essential tests into a portable, intelligent, and connected device, it enables early risk detection, real-time decision-making, and democratized access to quality diagnostics.
Whether deployed in hospitals, homes, or health outreach programs, this technology fosters timely intervention, patient empowerment, and a data-driven approach to chronic disease management. It bridges the gap between laboratory diagnostics and everyday health monitoring — paving the way for a more responsive, personalized, and preventive healthcare future.


.jpg)




-160x160-state_article-rel-cat.png)









-205x205.jpg)